Table of Contents

Introduction to Foot Peeling
Foot peeling, also known as desquamation of the feet, is a common dermatological issue that can be both unsightly and potentially problematic from a health perspective. Our skin serves as a protective barrier for our bodies, defending against various environmental factors, pathogens, and maintaining moisture levels. However, the skin on our feet is particularly susceptible to peeling due to factors like extreme heat, moisture, and dryness. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms of foot peeling, its causes, and various treatment options to help you manage this condition effectively.
Symptoms of Foot Peeling
Foot peeling often presents with a range of symptoms, which may include:
- Itchiness: Itchy skin on the feet is a common early symptom of foot peeling.
- Burning or Stinging: Some individuals with foot peeling experience a sensation of burning or stinging on their feet.
- Shedding of Skin: Foot peeling involves the shedding of the outer layers of skin on the feet, resulting in visible peeling or flaking.
- Dry Skin: The affected skin may appear dry and scaly, further contributing to the peeling process.
- Redness: Redness or inflammation of the skin on the feet can occur in conjunction with foot peeling.
These symptoms can vary in intensity, and their presence may depend on the underlying cause of foot peeling.
Causes of Peeling Skin on Feet
It can have various underlying causes, which can be categorized into different groups:
1. Environmental Causes
Environmental factors play a significant role in it. These causes are often related to lifestyle habits or external exposures, including:
- Trauma: Repeated irritation of the skin on the feet, such as from ill-fitting footwear, physical activity, or exposure to chemicals in soaps and detergents, can lead to it.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors like extreme heat, cold, wind, sun exposure, humidity, and dryness can all contribute to it. For example, a sunburn can lead to excessive dryness, which, in turn, results in peeling skin on the feet.
- Bodily Function: The body naturally sheds skin cells, and the feet are prone to a build-up of dead skin cells, which can contribute to it.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal infections, such as Athlete’s foot, thrive in warm, moist environments, making them a common cause of it.
- Allergies: Certain substances can trigger allergic reactions on the skin of the feet, leading to it.
2. Inflammatory Causes
It can also result from bacterial infections, which can lead to inflammation and skin shedding.
3. Systemic Disease Causes
In some cases, it may be associated with underlying medical conditions, including:
- Hereditary Conditions: Certain inherited conditions can manifest with it as a primary symptom, although these conditions are often underdiagnosed due to their mild symptoms.
- Cancer: It can be a byproduct of cancer itself or a side effect of cancer treatment methods.
It is important to note that it can have various underlying causes, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause in your case.
Common Skin Conditions Associated with Foot Peeling
It can sometimes be a symptom of underlying skin conditions. Here are some skin conditions commonly associated with it:
1. Non-specific Dermatitis (Skin Inflammation)
Non-specific dermatitis, also known as contact dermatitis, is characterized by inflammation of the skin due to various causes. It can result from skin contact with substances that provoke a reaction, such as plants, soaps, jewelry, and fabrics. Symptoms often include red, swollen, itchy rashes with blistering and oozing.
2. Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to direct contact with irritating substances, such as soap, bleach, cleaning agents, chemicals, or water. Symptoms include swollen, stiff, dry, cracked skin with painful open sores.
3. Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis arises when the skin comes into contact with substances that trigger allergic reactions, such as nickel, poison ivy, or certain perfumes. It results in red, itchy, scaly, and flaking skin.
4. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Atopic dermatitis, commonly referred to as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by an itchy rash. It often affects infants and young children, presenting as dry, scaly rashes on the scalp, forehead, cheeks, elbows, knees, and buttocks.
5. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection of the feet and toes, typically caused by warm, moist environments and communal showering. Symptoms include foot redness, itching, skin changes, and peeling between the toes.
6. Normal Occurrence of Dry Skin
Dry skin can be a common occurrence, resulting from factors like overheating in winter, air conditioning in summer, aging (loss of sweat and oil glands), and excessive use of soap, antiperspirants, perfumes, and hot baths.
7. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, leading to a slowed metabolism. Symptoms include fatigue, feeling constantly cold, weight gain, slow heart rate, and depression.
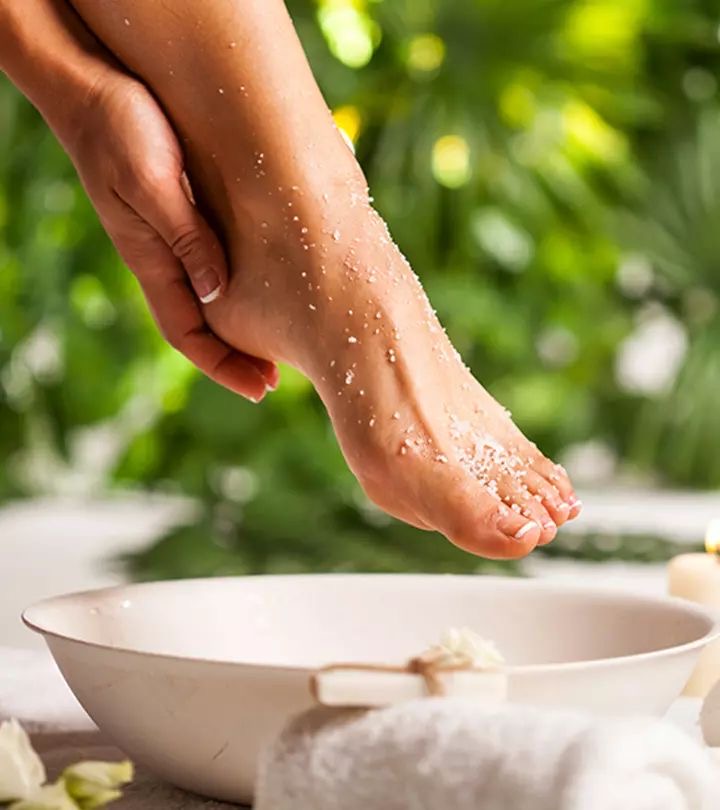

Treatment Options for Foot Peeling
Treatment for it depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some treatment options and strategies:
At-Home Treatments:
You can initiate treatment for foot peeling at home using the following remedies:
- Warm Water and a Scrub: Soak the affected feet in warm water for up to 20 minutes to soften the skin, making it easier to gently scrub away dead skin.
- Moisturizer: Apply moisturizing lotion or cream to the affected areas multiple times a day to keep the skin hydrated and reduce peeling.
- Hygiene: Maintain proper foot hygiene by keeping your feet clean and dry to prevent fungal infections. Wear clean socks and well-ventilated shoes, especially in public areas like swimming pools.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Over-the-counter powders or creams designed to treat conditions like athlete’s foot can help alleviate it’s symptoms.
Medical Treatments:
In more severe cases of it or when an underlying medical condition is diagnosed, medical treatments may be necessary. These treatments can include:
- Oral Antifungal Medications: If a fungal infection like Athlete’s foot is the cause, your doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medications to combat the infection.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections associated with foot peeling, antibiotics may be prescribed to address the underlying infection.
- Prescribed Foot Creams: Topical creams or ointments with prescription-strength ingredients may be recommended by your doctor to manage it.
When to See a Doctor:
It’s advisable to consult a doctor if you experience the following:
- Severe Pain: If it is accompanied by severe pain or discomfort, seek medical attention.
- Persistent Peeling: If it does not improve or subside within two to four weeks of at-home treatment, consult a healthcare professional.
- Fever: The presence of a fever along with foot peeling may indicate an underlying infection, requiring medical evaluation.
- Concerns about the Cause: If you are uncertain about the cause of it or suspect an underlying medical condition, it’s essential to consult a doctor for a thorough evaluation.

Conclusion
In conclusion, it is a common skin condition with various potential causes. While many cases can be managed effectively with at-home treatments, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe symptoms, persistent it, or have concerns about the underlying cause. With proper care and treatment, you can alleviate it and maintain healthy, comfortable feet.
Share this content:









